HexOperate
Introduce
This tool is used for hexadecimal data manipulation, which can be converted to binary for operation, and supports binary bit operations and logical operations
How to use
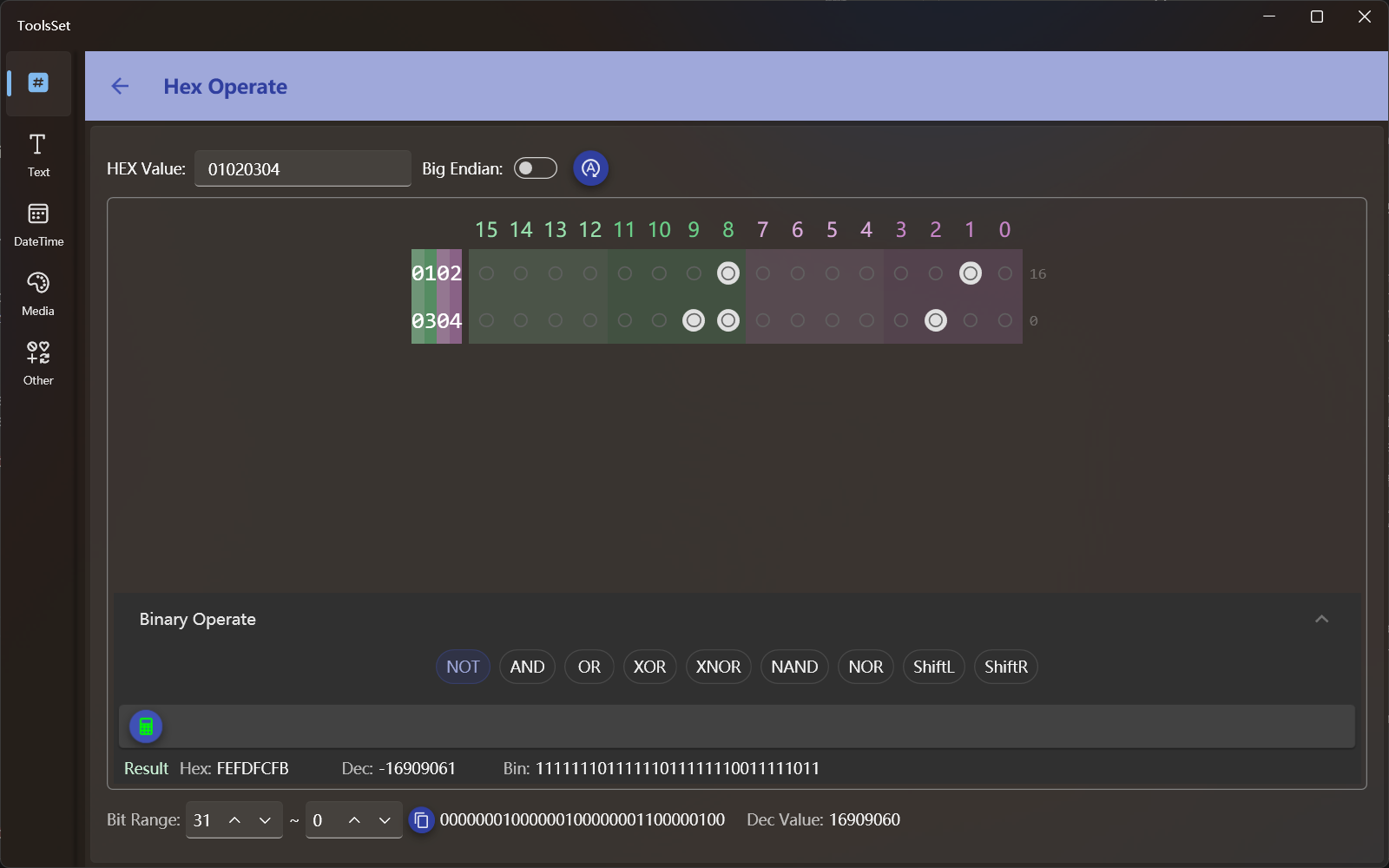
Operand setting: You can enter hexadecimal number in the top text box, the right side is the endian switch, the switch can be turned on to reverse the bytes order, and after the operand set, you need to click the right button to update the value to the binary data area below
The number in the input box is 4 digits by default, and it is converted to binary is 16 bits, the number of digits in the binary region can be changed by changing the number of digits in the hexadecimal data
For example, if you enter a 5-digit hexadecimal number, the number of digits in the binary region will become 32 bits, and the hexadecimal data will be automatically filled to 8 bits
Enter the 9-digit hexadecimal number, the number of digits in the binary region will become 64 bits, and the hexadecimal data will be automatically filled to 16 bits; The same can be done to reduce the number of digits
Hexadecimal data supports up to 16 bits, i.e. up to 64 binary bits
Binary operation
Each bit in the binary area is a switch, and the corresponding bit value can be set to 1 or 0 by turning it on and off
When the switch is turned on or off, the changes to the values are automatically synchronized to the upper hexadecimal data and the lowest bit range data
Logical operations
Below the binary area is the logical operation area, which can perform bitwise logic operations. This area is not expanded by default, and you can click the section title bar to switch when you need to operate
Actions you can perform in this area include:
- Single operand operation
- NOT: Bitwise negation of binary data
Click the Update Data button at the top to automatically update the value, if you modify the binary bits, you need to click the Calculate button in this area to recalculate the value
- ShiftL: Shift the binary data to the left bits, and operate through the slider, and the data range is the same as the number of binary digits of the current data
- ShiftR: Shifts binary data to the right bits, and the operation is the same as that of ShiftL
When shift to right, you can choose whether to shift with the sign through the switch on the right, and the default is on = shift right with the sign
- NOT: Bitwise negation of binary data
- Two operand operations
- AND
- OR
- XOR
- XNOR
- NAND
- NOR
This set of operations is the same, first click the button to select the operation you want to perform, then set the second operand, and then click the calculate button to get the result
There are three ways to input the second operand: hexadecimal, decimal and binary, the hexadecimal and decimal values can be entered directly in accordance with the format
Binary input is a set of on/off buttons that can be increased or decreased count by varying the number of data bits
The data of these three bases will be automatically converted, that is, if you modify one value, the value of the other base will be automatically update
- Single operand operation
Get the bit range value
The bottom area can get the value of the selected range by bits, and the default bits are all bits, and you can get some of them by modifying the start and end bits
The start and end bits are interchangeable, and the bits obtained after the swap will also be in reverse order
You can click the copy button in the middle to copy the intercepted binary data
